HIMP 2030 steers Malaysia’s halal industry towards global prominence

The Halal Industry Master Plan (HIMP) 2030 serves as a blueprint for comprehensive growth, aiming to strengthen Malaysia’s leadership in the global halal industry and drive socioeconomic progress.

Halal Development Corporation (HDC) Chairman Khairul Azwan Harun explained that HIMP 2030 was developed to catalyse the comprehensive growth of Malaysia’s halal industry by the Ministry of Investment, Trade and Industry (MITI), with strategic support from HDC.
“The HIMP’s theme, ‘Prominent, Visible and Globalised Halal Malaysia,’ represents the nation’s aspiration to strengthen its leadership in the world’s halal industry and achieve socioeconomic progress,” said Azwan.
“HIMP 2030 also aims to advance Malaysia’s participation in the halal industry globally. It positions the industry as a lucrative and competitive opportunity, further develop a dynamic halal industry ecosystem that advances Malaysia’s products and services, and contribute positively to the growth of Malaysia’s socioeconomic wellbeing.”
STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK
Under HIMP 2030, 23 initiatives have been identified to anchor the seven (7) strategic thrusts and address all identified opportunities and challenges.

These seven strategic thrusts include:
• Enhancing halal-friendly policy and legislation.
• Creating new and bigger market spaces for Malaysia’s halal products and services.
• Establishing a larger pool of halal experts and professionals to meet global needs.
• Enhancing the quality and integrated infrastructure development fostering thought leadership.
• Fostering thought leadership.
• Producing more home-grown halal champions.
• Facilitate more competitive participation of bumiputeras in the halal industry.
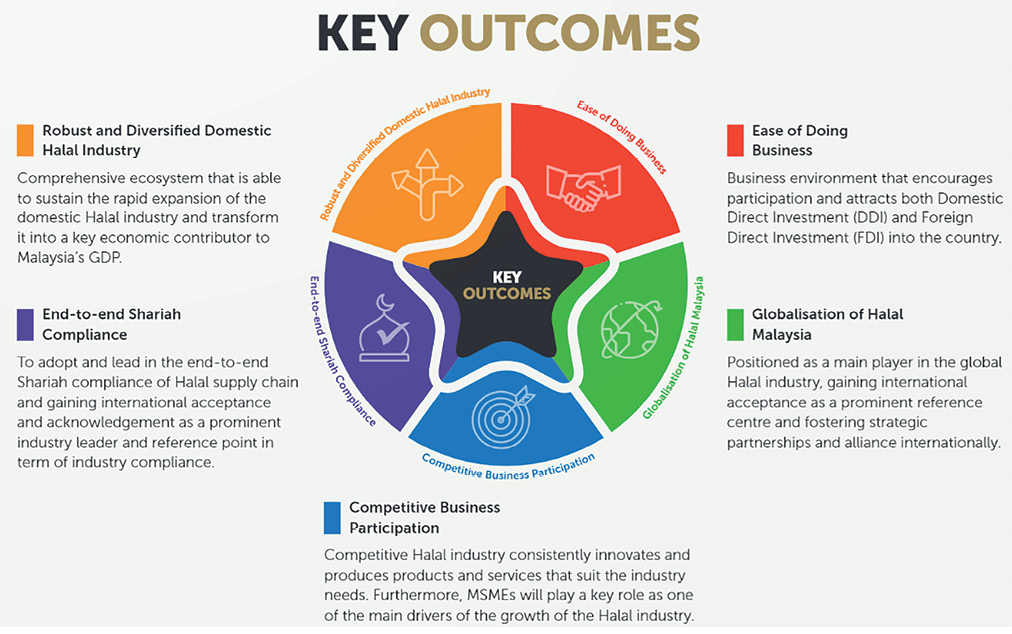
These initiatives are expected to be driven by the five key outcomes of HIMP 2030, which include:
• Having a robust and diversified domestic halal industry.
• Possessing end-to-end Shariah compliance.
• The ease of doing business in Malaysia.
• Competitive business participation.
• The globalisation of Halal Malaysia.
Phase A (2023-2025) of HIMP 2030 is underway, with efforts to build momentum, broaden expertise, and penetrate domestic and global markets.
Azwan stated: “Additionally, the master plan outlines the development of the domestic halal industry to foster local champions capable of capturing the global halal market and establishing themselves as significant players across the halal industry supply chain.
“This strategic direction aligns with HDC’s vision of ensuring halal businesses are the preferred choice.
“HIMP 2030 lays the foundation for Malaysia to emerge as a global leader in the halal industry, contributing significantly to the nation’s socioeconomic wellbeing.”
CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS
Leveraging the current halal ecosystem in Malaysia, the domestic halal industry aims to contribute 10.8 per cent towards Malaysia’s total gross domestic product (GDP) by 2030.
However, Azwan highlighted that several challenges and opportunities have been identified within the domestic and global halal industry.
Challenges hindering the implementation of HIMP 2030 include:
i. Low awareness of Halal Industry development; the focus is still strong on the Halal management perspective, particularly in certification and standard development, such as product R&D and innovation.
ii. Poor coordination to develop comprehensive policies and strategic thrusts for the halal industry.
iii. Resources provided were not streamlined, making it difficult to control, monitor and report halal-related programmes and performance.
iv. Lack of data on halal limits the capability to produce comprehensive analyses and reports which can assist the government in making informed decisions.
v. Wrong perception of the value and importance of halal by industry players
vi. Duplication of roles among agencies
Not all halal-related activities are eligible for tax incentives (e.g., Manufacturing or bottling of beverages).
viii. Tax incentives offered for the halal sector vary and are not streamlined. Each Investment Promo Agency, like MIDA Corridors, has its own set of incentives.
ix. Tax incentives are given based on activities for companies investing in HALMAS Status Parks rather than companies.
x. Investors buy land in Halal Parks but do not develop or conduct any activities in the park. This has caused land speculation, where investors buy for investing purposes without intending to conduct business activities.
However, he emphasised HDC’s proactive approach to addressing these challenges through the strategic thrusts and initiatives outlined in the master plan.
By fostering collaboration, streamlining policies, and enhancing awareness, HDC aims to overcome obstacles and ensure the successful execution of HIMP 2030.
ENVISIONING THE FUTURE
Looking ahead, HDC envisions a dynamic and thriving future for Malaysia’s halal industry, characterised by sustainable growth, innovation, and global competitiveness.

Azwan emphasised HDC’s commitment to promoting sustainable growth, fostering innovation, enhancing global competitiveness, and developing Halal talent.
“HDC aims for sustainable growth in Malaysia’s halal industry, focusing on increasing the industry’s contribution to the national economy (GDP) while ensuring environmental and social sustainability.
“This includes expanding the halal market domestically and internationally, fostering entrepreneurship, and creating employment opportunities.
“HDC also recognises the importance of innovation and technology adoption in driving the growth and competitiveness of the halal industry.
“HDC aims to promote research and development activities, encourage the adoption of cutting-edge technologies such as loT, big data, Blockchain and IR 4.0 in halal production processes, and foster innovation in halal products and services.
“HDC is committed to enhancing Malaysia’s global competitiveness in the halal industry. This involves strengthening the country’s position as a leading halal hub by improving infrastructure, streamlining regulatory processes, and enhancing the quality and credibility of Malaysia’s halal certification system.
“HDC also aims to promote Malaysia as a halal innovation and excellence centre, attracting investment and talent.
“Finally, HDC recognises the importance of halal talent development in driving the growth and sustainability of Malaysia’s halal industry.
“HDC aims to devote to skills development, education, and training programs to build a skilled workforce capable of meeting the demands of the halal industry.
“This includes supporting entrepreneurship and fostering a culture of innovation within the halal sector.”
COLLABORATIONS AND INITIATIVES
Strategic collaborations and innovative initiatives aim to promote Malaysia as a leader in the halal economy, foster international partnerships, and enhance industry competitiveness.
Azwan highlighted HDC’s collaborations with various international organisations, governments, and industry players to strengthen halal trade and investment ties.
Partnerships with countries like Indonesia, Vietnam, Cambodia, Japan, China, Korea, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, and the EU underscore Malaysia’s commitment to global halal industry leadership.
Recent collaborations in Osaka, Japan, demonstrate HDC’s commitment to supporting the global expansion of halal practices and expertise, further solidifying Malaysia’s position as a leader in the halal industry.
Looking ahead, Azwan outlined HDC’s ongoing projects aligned with the HIMP 2030, each designed to propel Malaysia towards halal industry excellence:
Majlis Pembangunan Industri Halal (MPIH) – Enhancing halal industry-friendly policies and legislation to support growth and innovation.
Malaysia Global Halal Showcase – Creating new market opportunities for Malaysian Halal products and services through global exhibitions.
Training Courses for Certified Halal Executive and Auditing Programme – Building a skilled workforce of Halal experts to meet global demand.
New HALMAS – Investing in quality infrastructure to improve competitiveness and efficiency in the Halal industry.
World Halal Business Conference – Facilitating thought leadership and dialogue among industry stakeholders to shape the future of the Halal economy.
Halal Sourcing Partnership Programme – Supporting the growth of Halal businesses, particularly among Bumiputera entrepreneurs, through strategic partnerships.
These initiatives align with the strategic objectives of HIMP 2030, driving Malaysia’s Halal economy towards global prominence and fostering sustainable growth.
Malaysia’s halal industry is primed for unprecedented growth and international prominence. Therefore, Malaysia’s aspirations to become a global Islamic finance hub have come to the forefront, said Halal Development Corporation (HDC) Chairman Khairul Azwan Harun.
Azwan, who assumed his role in May 2023, highlights the government’s steadfast commitment to nurturing the halal industry.
“Over the past decade, Malaysia has consistently secured the top spot in halal F&B, Islamic finance, and recreational and media sectors, according to Dinar Standards’s State of the Global Islamic Economy Report.
“This achievement underscores Malaysia’s stature as a global leader in halal standards and practices.”
With over 40 years of dedication to establishing gold standards in Halal, Malaysia has become a beacon for other halal markets worldwide.
The ecosystem serves as a blueprint for emulation, propelling Malaysia towards achieving Toyyib status—a testament to its unwavering commitment to quality and integrity in the halal industry.
HDC’s strategic roadmap, the Halal Industry Master Plan (HIMP) 2030, is a blueprint for Malaysia’s journey towards becoming a prominent global halal hub.
Projections indicate that the halal industry’s contribution to Malaysia’s GDP will surpass 10.8 per cent, with the potential for even greater expansion. The anticipated US$5 trillion global halal market by 2030 presents a significant opportunity for Malaysia to capitalise on, with only 20 per cent of the market currently being tapped.

Azwan expressed confidence that with the proper execution and spirit, Malaysia will meet and exceed these targets.
Azwan emphasizes the importance of collaboration and innovation in meeting the growing demand for halal products worldwide.
Markets in North America, China, Japan, Korea, and the Middle East are increasingly turning to Malaysia for halal-certified goods and services. The Department of Islamic Development Malaysia’s (JAKIM) halal certification is recognised globally, making it a preferred choice for multinational corporations seeking to penetrate diverse markets.
FOSTERING COLLABORATIVE ECOSYSTEM
HDC’s role extends beyond mere facilitation; it actively fosters an inviting ecosystem to attract multinational corporations to Malaysia.
By positioning Malaysia as an export hub for finished halal products, the nation can significantly boost its exports and achieve its ambitious targets by 2030.
Moreover, this initiative is not just about economic growth but also about creating high-income employment opportunities, particularly for the younger generation, thus driving socio-economic development.
With a robust infrastructure, commitment to excellence, and strategic initiatives like HIMP 2030, Malaysia is on track to realise its vision of becoming the foremost global halal hub, driving economic prosperity for the nation and its people. – 









