Being overweight and obese are closely linked to an increased risk of infections, apart from other medical conditions which may lead to higher lethality

BY ASSOC PROF DR TAN TOH LEONG

AND BY DR LOO SAY YEE
Many studies showed that obesity and being overweight are closely linked to an increased risk of infection in various parts of our body.
The risk of infection in the organs involved in breathing starts from the nose, throat, sinuses, windpipe and all the way to the lungs. Recent data from the Covid-19 pandemic showed that obesity contributes to an increased risk of lung infection with a poorer prognosis, resulting in higher mortality.
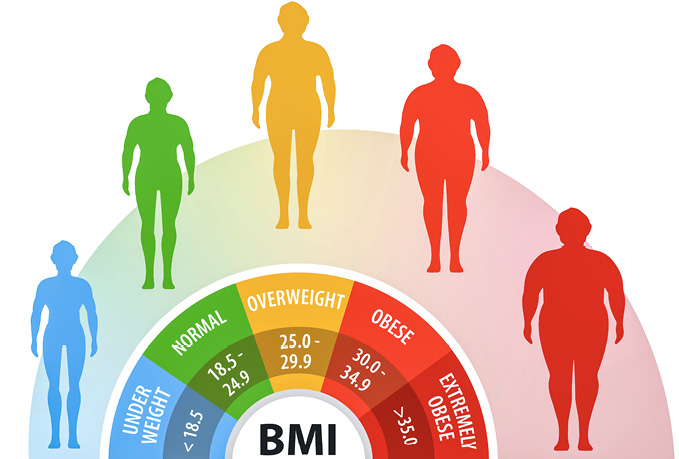
Obesity means excessive fat storage in our bodies. We measure our body fat using the body mass index (BMI) that applies to adult men and women. It is calculated by a person’s weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters. For adults, a BMI of 25 to 29.9 kg/m2 is considered overweight and ≥30 kg/m2 is obese. As for children, age is important in deciding whether they are overweight and obese.
 Thus far, the underlying causes of obesity-related vulnerability to infection are not well established. However, some studies showed that vitamin D deficiency and the destruction of immune responses are contributing factors.
Thus far, the underlying causes of obesity-related vulnerability to infection are not well established. However, some studies showed that vitamin D deficiency and the destruction of immune responses are contributing factors.
Destruction of the natural and acquired immune responses among overweight and obese individuals results in chemical imbalance in the fat tissue. It causes a rise in inflammation and a decrease in the immune response.
Vitamin D deficiency is a common condition among individuals with obesity. It affects the immune system and increases the risk of infection.
Common infections
Besides that, changes in the lung physiology in obese individuals increase the work of breathing and lung efficacy. The effects are more prominent when they become unwell.
 Disruption of the skin barrier function in obese individuals results in poor healing and reduced immune response. Being overweight and obese cause an increased risk of getting diabetes which increases the risk of infection tremendously.
Disruption of the skin barrier function in obese individuals results in poor healing and reduced immune response. Being overweight and obese cause an increased risk of getting diabetes which increases the risk of infection tremendously.
Moreover, they are also more vulnerable to heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol and stroke. Lastly, overweight and obese individuals have bigger body habitus, affecting drug distribution, absorption and treatment efficacy.
Bladder and kidney infections are among the most common infections in the community and in hospitalised patients. Those who are diabetic and obese are at a higher risk of getting these infections.
Bacterial and fungal skin infections are also common among individuals who are overweight and obese, particularly at the breast folds, armpits, belly folds, groins, buttocks, and nail and nail beds. This phenomenon is not only present among adults, but also in children.
Adopt a healthy lifestyle
Moreover, post-operative surgical site infections are inevitable among overweight and obese patients. Hence, they are usually treated prophylactically to prevent wound breakdown and slow wound healing.
Apart from the risk of infections, obesity has evolved globally as a major health risk for non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, leading to the risk of heart disease, stroke and inevitably, death. Being a person with diabetes puts one at risk of kidney failure requiring dialysis, blindness, recurrent infections and leg amputation.
Back pain or knee pain due to osteoarthritis can happen with excess weight. The risk of cancer is also markedly increased among those who are overweight and obese.
Being overweight and obese are closely linked to an increased risk of infection, apart from other medical conditions which may lead to higher lethality. Therefore, we should adopt a healthy lifestyle in terms of wiser food choices and adequate exercise to prevent and reduce the risk of being overweight and obese and its related complications. – The Health
Associate Professor Dr Tan Toh Leong is a Senior Lecturer and Consultant Emergency Physician in Hospital Canselor Tuanku Muhriz, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM) and President & Founder of Malaysian Sepsis Alliance (MySepsis), while Dr Loo Say Yee is Trainee Lecturer in Family Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, UKM and Committee Member of MySepsis








