
Your way towards environmental sustainability
Carbon footprinting has caught the interest of most entities looking to showcase leadership in green initiatives
By Wan Mazlina Wan Hussein & Mohd Nazri Ahmad
Carbon Footprint
One of the environmental impacts affecting the planet that garners global attention is climate change (global warming). Efforts and initiatives at all levels, be they international, regional or national, are being actively discussed and implemented to reduce the emission of greenhouse gases (GHG) into the atmosphere.
The world’s carbon equivalent emissions or GHG emissions are caused by burning fossil fuel for power, heat, transportation, and agriculture. The main sources of global warming in Malaysia are the energy, transport, manufacturing and construction sectors.
LCA’s single-impact category measurement
As an environmental assessment technique, the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is considered more academic than practical business use. However, carbon footprinting has caught the interest of most entities looking to showcase leadership in green initiatives towards managing the environmental sustainably.
The LCA approach is considered to avoid shifting environmental burdens from one stage to another throughout the life cycle chains.
Carbon footprinting is based on the principle of the LCA, focusing on a single impact category, i.e. global warming potential.
The results of carbon emissions, aka carbon footprint, associated with an activity, a process or a product derived from raw material extraction, energy and utilities consumption, transportation of materials and disposal of wastes as a complete cradle-to-grave approach will determine the global warming potential of the system, which will eventually translate into its impact to the climate change.
Carbon footprint measurement is a quantitative measure of a certain level of activities that results in GHG emissions. In carbon footprinting, considered activity data is multiplied by a carbon emission factor to derive the associated carbon equivalent emission from various GHGs.
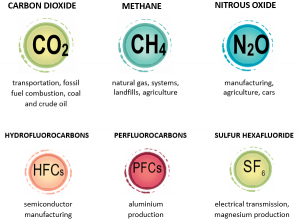
The commonly addressed or prominent GHGs are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O). The carbon emission factor is expressed in the unit of mass equivalent to carbon, i.e. kg CO2 equivalent (kg CO2 i.e. per functional unit).
The Carbon Footprint Edge
Carbon footprint is usually used in business-to-business communication.
Apart from that, its usage for business-to-consumer communication is trending with the avenue of carbon labelling. Carbon footprint would benefit both the supply and demand aspects, whereby:
- Businesses can communicate the environmental attributes of their products or services to their customers. Businesses can use carbon footprint results as a marketing tool to show that their products are better than their competitors in terms of environmental performance.
- Consumers can make informed decisions in their purchasing based on the environmental performance of products or services.
- Consumers are aware of how their purchased products or services contribute to carbon emissions and global warming.
- Initiatives towards carbon reduction can be translated into cost savings for both businesses and consumers.
Carbon footprinting provides options in its application. As a technique, it can measure the carbon footprint of the organisational system, value chain, process, product or supply chain.
Organisational Carbon Footprint
The principles and requirements of GHG emission quantification and reporting at the organisational level are as prescribed by the ISO 14064.
The organisational carbon footprint requirements include the design, development, management, reporting and verification of an organisation’s GHG inventory.
An organisational carbon footprint will help organisations understand carbon sources from their operations, including energy used by premises, processes and business travel.
Product Carbon Footprint
A product carbon footprint enables manufacturers to differentiate their products’ environmental performance from their competitors based on carbon equivalent value.
For a similar product category, having a lower carbon footprint value suggests that the product is more environmentally sustainable than the higher carbon footprint-valued products.
At the same time, carbon footprinting provides the avenue for the manufacturers to identify the environmental hotspots along its life cycle stages and improve the product’s carbon emission through carbon reduction options.
“Carbon footprint (CFP) of a product is the sum of GHG emissions and removals of one or more selected process of a product system, expressed as CO2 equivalent (CO2e) and based on life cycle assessment” – ISO 14067.
Providing Support for Environmental Performance Sustainability Assessment
SIRIM is one of the superior technology, quality, standards and certification providers in Malaysia. SIRIM, with its niche formation, acts as a one-stop centre for the environmental performance assessment of products and organisations from measurement, verification and certification to labelling.
The technical team in SIRIM’s Environmental Technology Research Centre (SIRIM-ETRC) provides technical support in conducting carbon footprint assessments using a toolkit developed in-house by SIRIM known as “SIRIM Karbon Kalkulator”.
The carbon footprint reports can be utilised by companies for third-party verification, certification and labelling by SIRIM QAS International.
SIRIM-ETRC is also responsible for the management of the Malaysia Life Cycle Inventory Database (MYLCID). MYLCID is an online database system providing life cycle inventory (LCI) results for materials, processes and systems pertinent to our country in terms of geographical and technological coverage.
LCI results comprise input and output flows which are essential in carbon accounting. Please visit https://mylcid.sirim.my to find out more.
SIRIM ECO-Labelling Scheme Towards greener building materials
The SIRIM Eco-Labelling certification is awarded by SIRIM QAS International, Malaysia’s leading testing, inspection and certification body.
SIRIM QAS is a member of the Global Ecolabelling Network (GEN), a non-profit network comprising 33 eco-label organisations worldwide, aiming to improve, promote and develop the eco-labelling of products and services worldwide.
SIRIM QAS’ membership in GEN gives credibility to the SIRIM Eco-Labelling Scheme. It puts it on par with the eco-labelling schemes of other member countries.
The most significant aspect of SIRIM Eco-Labelling scheme is the endorsement that a product has been independently evaluated. That enhances a brand’s image and the manufacturer’s reputation as an environmentally friendly company.
Further, reputable manufacturers will increase production efficiency and reduce wastage in terms of rejects. With the SIRIM Eco-Labelling mark, consumers need not carry out further tests as the product already complies with environmental standards.
Certified products not only give the assurance of environmental sustainability but also safety, quality and reliability.
The Eco-Labelling certification process is intensive. It involves enquiry, application, document evaluation, factory audit, sample selection and testing, recommendation and approval process, surveillance, and renewal.
Beyond just approval, the certification process also includes planned surveillance audits every two years and market surveillance to ensure that companies uphold the certification standards.
Upon certification, the brands can use SIRIM’s Eco-Labelling mark for marketing their products. It is an effective way to communicate a product’s environmental benefits to the consumers. It enables them to make better purchasing decisions based on eco-friendly attributes.
Having the mark provides a competitive edge for the brand over other similar ones in terms of eco-friendliness.
For organisations interested in obtaining SIRIM Eco-Labelling certification, visit www.sirim-qas.com.my or call +603-5544 6400 or e-mail us at cserviceqas@sirim.my









