Learning about the most complex organ in the human body is key to maintaining good health
BY KHIRTINI K KUMARAN
THE human brain is the most complex organ in the human body, and it is responsible for all the body’s functions.
How we respond, work and deal with people involves three different parts of the brain, which have established numerous interconnections through which they influence the operations of one another.

During a recent ‘Know Your Brain’ webinar organised by SuperTrouper360, its Founder Tony Pereira presented how the brain operates and how to keep it healthy.
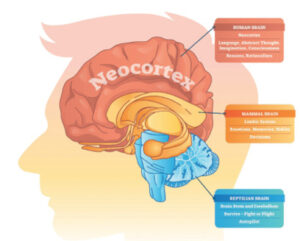
He said the first part was the reptilian brain, also known as the primitive brain, composed of the brain stem, cerebellum and basal ganglia. It is involved with primitive drives related to thirst, hunger, sexuality, and territoriality and controls the body’s vital functions such as heart rate, breathing, body temperature and balance.
Most importantly, it helps us respond to threats, which could either be an actual or perceived threat. So, the reptilian brain works with another part of the brain called the amygdala, the brain’s emotion centre.
“If the brain feels under threat, the amygdala acts as a panic button and immediately responds and starts working with the reptilian brain to decide how
they should respond to the situation,” said Tony.
“The amygdala and the reptilian brain will quickly assess the situation. And we are talking literally milliseconds before deciding what should be the appropriate response, which will either be flight, fight or freeze.”
The second part is the limbic system, which comprises the hippocampus, the amygdala, and the hypothalamus. The hippocampus plays an essential role in forming new memories about past experiences. Hypothalamus is associated with changes in emotional reactivity.
The limbic system operates as a quick automated response system, where one does not need to think and knows the answer immediately.
“It is where our memory is stored, so it will quickly refer to it and tell you the appropriate response to a particular situation,” he explained.
The third part is the prefrontal cortex, the cerebral cortex covering the front part of the frontal lobe. “It is also known as the CEO of the brain as it involves complex executive functions and cognitive behaviours, such as concentration, decision-making, abstract thinking, and reasoning.”
 Despite the complexity of the brain operations, Tony highlighted the brain was not designed to multi-task. Instead, it essentially switches tasks rapidly from one to another, then back again.
Despite the complexity of the brain operations, Tony highlighted the brain was not designed to multi-task. Instead, it essentially switches tasks rapidly from one to another, then back again.
“When you switch tasks from one to another, your brain goes under stress, which is minimal stress. But every time we switch from one to another, it puts the brain under stress.
“Now, when the brain is under stress, it releases the stress hormone cortisol, which kills the brain cells and slowly damages the brain.”
What kills brain cells
Brain cells, also known as neurons, are the building blocks of the human brain, which transmits information via electrical and chemical signals within the brain and throughout the body.
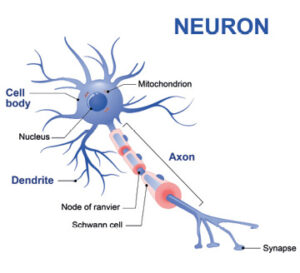 “On average, the human brain has about 86 billion brain cells, and we lose about three million brain cells daily, which sums up to almost 30 billion brain cells by age 50. Certain habits exacerbate this.”
“On average, the human brain has about 86 billion brain cells, and we lose about three million brain cells daily, which sums up to almost 30 billion brain cells by age 50. Certain habits exacerbate this.”
Stress, sleep deprivation, an unhealthy diet, and alcohol consumption are among the causes of damage and kill brain cells.
Tony also highlighted that excessive use of digital devices is killing our brain cells much faster than ever before.
“The more you use the brain, the stronger the connection. And if you stop using it, the connection gets weakened, and eventually, it will die.”
“There were surveys done by Reuters, which found that 46 per cent of the respondents said that they suffer from information overload from the internet, which causes stress and tension.”
This is because the brains get overwhelmed by the massive amount of information and fail to process it anymore.
Next is digital dementia due to the availability of information at the click of a button and where we are not required to remember information.
“Lastly is digital deduction, whereby the digital devices do the work and thinking for us, and we need to decide yes or no.
“Because of this, the brain cells are dying as they’re not being used. This is called pruning. Fortunately, we are also able to preserve and regenerate brain cells.
“We can create new brain cells to make up for the brain cells that we are losing, hence ensuring our brain does not drop efficiency or efficacy.” — The Health
How to preserve and generate brain cells
Exercising
Firstly, the most critical activity is exercising because it stimulates the growth of new connections and improves the impaired connection between brain cells.
While any form and level of exercise are encouraged, the most optimal practice is to exercise outdoors and do 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
“What the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is recommending is that when you are exercising, your heart is beating between 100 and 130 beats a minute. If you haven’t exercised before, I suggest starting slow,” said SuperTrouper360 Founder Tony Pereira.
Learn new things
Research was done in London among drivers of London black taxis, who had to take a challenging course over three years, where they had to memorise 25,000 street names and 50,000 landmarks.
Brain scans of the hippocampus were taken before and after the course. The result showed that the hippocampus had grown simply because of the new facts learned, and new brain cells were created to accommodate the latest information.
Social connections
The third way is to form social connections as the brain loves connecting with people. Experiments with animals have shown that solitary confinement animals have low neural activity. In comparison, animals in large groups have a higher level of brain activity. It also explains why there were many cases of people feeling depressed during the pandemic.
Sleep
Sleep is one of the most important things you can do to generate new brain cells.
“When you sleep, memories stored in the hippocampus are distributed to other brain parts. So, if you don’t get enough sleep, the hippocampus will lose the information you learned during the day.
“Scientists have also found that cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) clears the brain of the toxins developed during the day during our sleep. Therefore, these toxins accumulate over time when you do not have enough sleep.”
Diet
The brain only weighs about two per cent of the total body weight, but it consumes about 30 per cent of the food that we take. So, if we eat well, we’re sending good nutrients to the brain.
The other important point is hydration, as the brain is almost 80 per cent of water. Give the brain sufficient hydration to ensure it performs at its optimum level.
Mindfulness
Mindfulness increases the grey matter in the brain, which contains most of the brain’s neuronal cell bodies. It also helps the body centre, focuses our mind from wandering thought to thought, and helps retain information. — The Health








